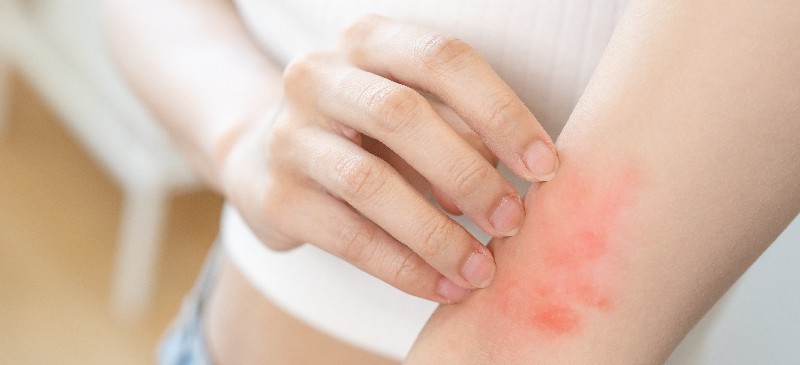
Allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) is a common skin condition characterized by an allergic reaction triggered by contact with a specific substance (allergen). This reaction manifests as red, itchy, and inflamed skin, often appearing within hours to days after exposure to the allergen. Identifying and avoiding the allergen is key to managing ACD, and various treatments can help alleviate symptoms and promote healing. In this blog post, we will explore the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and effective treatments for allergic contact dermatitis. Betnovate C Cream Uses and Betnovate Gm Cream is an applied cream used to treat skin conditions such as dermatitis, psoriasis, eczema, and allergic contact dermatitis.
Causes and Symptoms of Allergic Contact Dermatitis
Causes:
- Allergens: Common allergens that can trigger ACD include metals (e.g., nickel in jewelry), cosmetics (e.g., fragrances, preservatives), topical medications (e.g., neomycin), plants (e.g., poison ivy, poison oak), latex, and certain chemicals (e.g., formaldehyde).
Symptoms:
- Itching: Persistent itching is a hallmark symptom of ACD and can range from mild to severe.
- Redness: The affected skin area appears red or pink due to inflammation.
- Swelling: Swelling may occur, especially in more severe cases or with repeated exposure.
- Blisters: Small fluid-filled blisters may develop, which can be painful and may ooze.
- Dryness and Scaling: The skin may become dry, scaly, and cracked, especially if scratching persists.
Diagnosis of Allergic Contact Dermatitis:
Diagnosing ACD typically involves a thorough evaluation of the patient’s medical history, symptoms, and potential exposures to allergens. A dermatologist may perform the following:
-
Skin Examination:
- The dermatologist will examine the affected skin areas to assess the appearance of the rash, distribution pattern, and severity of symptoms.
-
Patch Testing:
- Patch testing is a specialized diagnostic test used to identify specific allergens causing ACD. Small amounts of potential allergens are applied to patches, which are then placed on the skin for a period of time (usually 48 hours). Reactions are assessed after the patches are removed.
-
Elimination Diet (if applicable):
- In cases where food allergens are suspected, an elimination diet may be recommended to identify and avoid triggering foods.
Treatment Options for Allergic Contact Dermatitis:
Effective treatment of ACD focuses on relieving symptoms, reducing inflammation, identifying and avoiding allergens, and promoting skin healing. Treatment options include:
-
Avoidance of Allergens:
- Identify and Eliminate: Once allergens are identified through patch testing or history, avoid contact with these substances to prevent further irritation and recurrence of symptoms.
- Substitute Products: Choose products labeled as hypoallergenic, fragrance-free, and suitable for sensitive skin to minimize the risk of triggering ACD.
-
Topical Treatments:
- Corticosteroids: Topical corticosteroids are the mainstay of treatment for ACD. These medications reduce inflammation, itching, and redness. They are available in varying strengths, and the dermatologist will prescribe the appropriate potency based on the severity of symptoms and location of the rash.
- Topical Calcineurin Inhibitors: In cases where corticosteroids are not suitable or effective, topical calcineurin inhibitors (such as tacrolimus or pimecrolimus) may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and itchiness.
-
Moisturizers:
- Emollients: Regular application of moisturizers helps repair the skin barrier and alleviate dryness associated with ACD. Choose fragrance-free and hypoallergenic formulations to minimize irritation.
-
Cool Compresses:
- Applying cool, wet compresses to the affected areas can provide relief from itching and inflammation. Avoid hot water, as it can exacerbate symptoms.
-
Oral Antihistamines:
- Non-Sedating Antihistamines: Oral antihistamines like cetirizine, loratadine, or fexofenadine may be used to alleviate itching and reduce allergic reactions. These medications are particularly helpful when itching disrupts sleep or daily activities.
-
Barrier Creams:
- Zinc Oxide or Calamine: Barrier creams containing ingredients like zinc oxide or calamine can soothe irritated skin and provide a protective barrier against further allergen exposure.
-
Wet Wraps:
- Wet Wrap Therapy: In more severe cases, wet wrap therapy may be recommended. This involves applying a moisturizer or topical medication to the skin, followed by a layer of wet gauze or clothing, and then a dry layer. It helps hydrate the skin, reduce inflammation, and enhance the absorption of topical treatments.
-
Steroid Injections (if severe):
- In cases of severe ACD or when large areas of the body are affected, a dermatologist may administer corticosteroid injections to rapidly reduce inflammation and symptoms.
Self-Care and Prevention Strategies:
-
Gentle Skin Care:
- Use mild, fragrance-free cleansers and moisturizers to avoid further irritation.
- Pat dry (do not rub) your skin after bathing to minimize friction and protect the skin barrier.
-
Protective Clothing:
- Wear protective clothing (such as gloves or long sleeves) when handling potential allergens or working outdoors.
-
Sun Protection:
- Use sunscreen with broad-spectrum SPF 30 or higher to protect sensitive skin from UV rays, which can exacerbate inflammation and damage skin barrier function.
-
Consultation with Dermatologist:
- If symptoms persist despite self-care measures or worsen over time, consult a dermatologist for further evaluation and treatment recommendations.
Conclusion:
Allergic contact dermatitis can significantly impact quality of life due to itching, discomfort, and skin inflammation. Effective treatment involves identifying and avoiding allergens, using topical medications like corticosteroids or calcineurin inhibitors to reduce inflammation, and practicing gentle skin care. By following these treatment strategies and preventive measures, individuals with ACD can manage symptoms, promote healing, and prevent future allergic reactions. Always consult with a healthcare provider or dermatologist for personalized advice and treatment options tailored to your specific condition and skin type. With proper management, many individuals can effectively control allergic contact dermatitis and maintain healthy skin.